1. Medical Clothing Types
Scrubs: Worn by healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, and technicians, scrubs are typically made from durable, easy-to-clean fabrics like cotton and polyester blends. They are designed for comfort, flexibility, and the ability to withstand frequent laundering in high-temperature environments, which is essential for sterilization. Scrubs are often color-coded to signify different roles or departments within a hospital.
Lab Coats: Worn by doctors, scientists, and lab technicians, lab coats are usually made from lightweight, breathable materials that can resist chemicals and bodily fluids. Their primary purpose is to protect wearers from contaminants while maintaining a professional appearance.
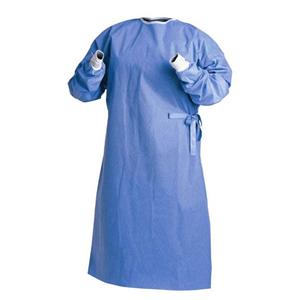
Surgical Gowns: Surgical gowns are critical in operating rooms. These are typically made from fluid-resistant or fluid-proof materials, such as tightly woven cotton or non-woven synthetic fibers. They are designed to provide a sterile barrier, protecting both the patient and the healthcare worker from the transmission of infections during surgical procedures.
Patient Gowns: These are designed for patient comfort and access during medical examinations and procedures. Often made from soft, lightweight materials, patient gowns are designed to be easy to put on and take off while providing adequate coverage and modesty.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): In recent years, the use of PPE has become more widespread due to the COVID-19 pandemic. PPE includes items like isolation gowns, gloves, face masks, and face shields, all designed to protect healthcare workers from infectious diseases. PPE fabrics are typically non-woven and treated to be impermeable to fluids, ensuring maximum protection.
2. Fabric Types and Properties
Cotton and Cotton Blends: Cotton is often used in medical clothing for its comfort and breathability. However, pure cotton tends to absorb fluids, which can harbor bacteria. For this reason, cotton is often blended with synthetic fibers to enhance its durability and moisture-wicking properties.
Polyester: Polyester is widely used in medical fabrics because it is strong, durable, and resistant to shrinking and wrinkles. It also dries quickly and can be treated with antimicrobial finishes to inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Non-Woven Fabrics: Non-woven fabrics, such as polypropylene, are commonly used in disposable medical items like surgical masks, gowns, and shoe covers. These fabrics are lightweight, breathable, and inexpensive to produce, making them ideal for single-use applications that require a sterile environment.
Antimicrobial Fabrics: With the rise of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), antimicrobial fabrics are becoming more prevalent in medical clothing. These fabrics are treated with agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, helping to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
3. Hygiene and Sterilization
One of the most critical aspects of medical clothing and fabrics is the ability to be thoroughly cleaned and sterilized. Most medical fabrics must withstand rigorous washing at high temperatures and exposure to harsh chemicals to eliminate pathogens. For disposable items, fabrics are designed to be used once and then safely discarded, minimizing the risk of contamination.
4. Comfort and Functionality
While protection and hygiene are paramount, comfort is also a significant consideration in the design of medical clothing. Healthcare workers often work long shifts, so their uniforms need to be breathable, lightweight, and allow for ease of movement. Similarly, patient gowns need to be soft, non-restrictive, and comfortable to ensure patients feel at ease during their stay in a medical facility.
5. Innovation and Sustainability
The medical industry is seeing increasing innovation in fabrics, particularly in the development of eco-friendly and sustainable options. There is a growing demand for reusable medical textiles that can reduce waste without compromising on safety or hygiene. Some hospitals and manufacturers are adopting organic cotton, recycled polyester, and biodegradable fabrics to lessen the environmental impact of medical clothing.
Conclusion
Medical clothing and fabrics are vital components of the healthcare industry, ensuring safety, hygiene, and comfort for both healthcare workers and patients. These textiles are specifically engineered to meet the unique demands of medical environments, from infection control to durability and ease of use. As the industry evolves, there is a continued push towards more sustainable, protective, and innovative fabric technologies.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.